CENTRE FOR IN-Vitro fertilization
High standard. Technology. Teamwork. Trust.
Contact
Contact
Gavra Vukovića b.b, Podgorica
Dentistry: 020 227 227
Polyclinic: 020 227 224
Gynecology: 020 227 444
First IVF cycle was completed in February 2004.
First baby was born on 05/11/2004.
First baby from the frozen embryo in Montenegro was born on 16/11/2006.
DEFINITION OF IN VITRO FERTILISATION
Contemporary medical treatments.
IVF method is used in diagnosed cases where conventional sterility treatment didn’t succeed.
The method consists of controlled stimulation of ovulation, egg cell collection from the ovary follicles , egg cell fertilisation with previously collected sperm in the cultivating medium, and embryotransfer of fertilised egg cell.
“For the first time we have solved all the problems. We are at the end of the beginning, not beginning of an end.”
– Patrick Steptoe
Dr Patrick Steptoe announcing the birth of Louisa Brown – the first “test tube baby” in 1978. In England. This was one of the most notable advances in development of treatment methods for infertility.
INFERTILITY
Challenges of the new time.
Possibility of pregnancy in a single couple with normal fertility is 25% in every cycle. It is estimated that 80-90% of fertile couples manage to get pregnant during the first year, 95% during the second year. Approximately 10-15% of couples throughout the world have fertility problems.
Causes of infertility are numerous and can be male, female, combined or inexplicable.
Male factors:
Reduced or non-existent spermatozoid production
Abnormal spermatozoid function
Varicocele
Lifestyle factors
Hormonal disorders
Chromosomal defect
Reproductive system defects that occured in the fetal period.
Immunologic problems.
Female factors:
Ovulation disorders
Anatomical problems of reproductive system
Endometriosis
Reproductive system defects that occured in the fetal period.
Infections
Immunologic problems.
Inexplicable causes of infertility are encountered in 15% od cases after diagnostic screening.
Possible causes may be: timing of ovulation, inability of egg cell to descend through oviduct, spermatozoid fails to encounter an egg cell, disturbed zigot transport, implantation error, etc.
ESTABLISHING DNA DAMAGE: CONTEMPORARY ANALYSIS IN MALE FERTILITY TREATMENTS
Detection of spermatozoid DNA fragmentation degree
Genetic integrity of the spermatozoid is indispensable for regular embryo development. High degree of DNA fragmentation in spermatozoids can cause male infertility, without being evident from the common methods of semen analysis. Detection of DNA fragmentation degree in spermatozoids provides reliable information for: identification of infertility cause, assessment of prognosis for assisted reproduction.
Some cases of DNA fragmentation cannot be cured, but If the damage was caused by free radicals, then lifestyle changes and diet can reduce oxidative stress and , in some cases, help reduce the levels of DNA fragmentation.
Causes of spermatozoid DNA fragmentation
Oxidative stress is the major cause of spermatozoid DNA fragmentation . Increased DNA fragmentation can also be correlated with:
Infections
Leucocytospermia
Febrile states
Increased testicular temperature
Diet
Drug abuse
Smoking
Exposure to environmental pollution
Age
Varicocele
Recommended treatment includes use of antioxidative medications over the course of at least 90. If there is no improvement, doctor may recommend testicular biopsy of spermatozoid aspiration in order to reduce the chance of DNA fragmentation in selected spermatozoid.
PROCEDURES AND METHODS
Custom made approach.
Assisted reproduction technologies (ART) encompass all procedures that consist of direct extraction of egg cells from the ovary.
Although the number of said procedures is on the rise, the most frequent ones are still:
– IUI ( Intra uterine insemination) – sperm being processed in a specialized medium, and introduced into the uterus.
– IVF (In Vitro fertilization) – extraction of an egg cell, laboratory fertilization, and subsequent placement of fertilized egg cell in the uterus.
– ICSI (Intracytoplasmic sperm microinjection) – introducing the spermatozoid directly into the egg cell.
After completing the diagnosis, examinations and tests, patient can start with the procedure which revolves around three key elements: male gamete (spermatozoid) , female gamete (oocyte) and uterus.
The technique consists of several successive phases:
– Stimulation of follicular growth and development
– Ultrasound monitoring of follicular growth and endometrial thickness.
– Follicular puncture, aspiration, and egg cell selection.
– Male sample analysis
– Embryo culture
– Transfer of embryo into the uterus.
Stimulating follicular growth and development
Growth of high number of follicles is one of the most important prerequisites for successful realization of ART program.
Stimulatory medication is applied in different doses and time intervals.
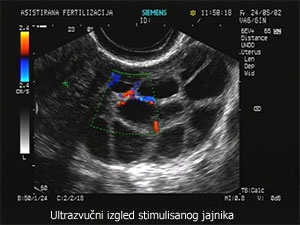
Ultrasound monitoring of follicular growth and endometrium thickness
Ultrasound examination is used for monitoring follicular growth in stimulated cycles in order to diagnose ovulation, measure daily follicular growth and determine the time for STOP injection administration.
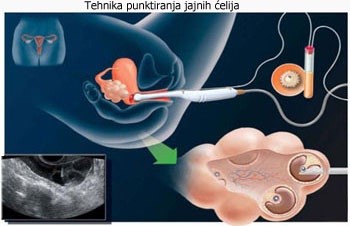
Follicular puncture, aspiration and egg cell selection
Puncture and aspiration are preformed via transvaginal route, as well as laparoscopically. Procedures can be preformed without anaesthesia ,with local anaesthesia and general anaesthesia. If preformed in local anaesthesia patient can simultaneously follow procedure live on screen.
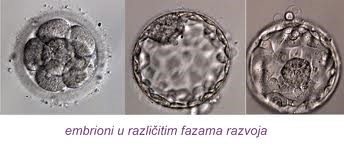
Embryo culture
Development and quality assessment of an embryo is monitored by the team of biologists during the period from aspiration to embryotransfer.
Embryo analysis is preformed again just before the embryotransfer. Based on quality criteria, embryos are selected for transfer or cryopreservation.
Embryotransfer
Embryotransfer is the final step following the laboratory phase, and it consists of embryo placement in uterus using specialized catheter.
Further development occurs naturally in the uterus until the childbirth.
INSEMINATION
Simplicity.
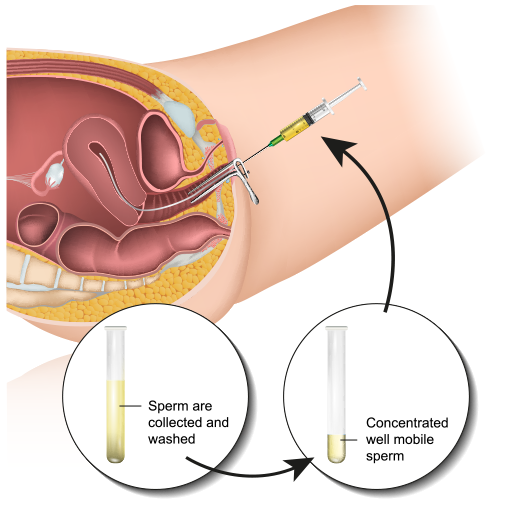
Although the method of insemination is chosen according to the spermatogram parameters and other relevant couple details, the difference in efficacy among various different techniques is minimal.
Most frequent modification of insemination is Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) with unprocessed or processed semen.
Insemination may be homologous (using partners semen) or heterologous (using donor semen).
The most frequent indication for insemination is reduced male fertility, low sperm mobility , quality of cervical mucus or presence of antispermatozoidal antibodies.
It can be preformed in natural or stimulated cycle.
CRYOPRESERVATION
Solution for the future.
Cryopreservation is process of controlled cell or tissue freezing to temperature below -80 °C and preservation at liquid nitrogen temperature of -196°C.
Low temperature stops all biologic activity including biochemical reactions leading to cell death.
Cryopreservation is also used in sterility treatment, mainly for sperm freezing, testicular tissue freezing, and excess embryo freezing (during the course of IVF treatment).
During the process of freezing, the freezing medium is enriched with cryoprotectants.
Cryoprotectants are substances with low freezing point which disable creation of ice crystals that could damage the cells. Different kinds of cryoprotectants are used for different stages of embryo development. Embryos can be frozen from the stadium of pronucleus until the blastocyst stadium (5-7 days after fertilization)
During the IVF treatment, there is a possibility of obtaining multiple vital embryos of good quality. The number of embryos can be higher than the couples requirement, in which case a cryopreservation is offered.
Cryopreservation can be preformed using method of slow freezing or rapid freezing (vitrification). The advantage of vitrification is that it provides better embryo quality , higher rate of embryo survival – and therefore higher percentage of pregnancies.
Our clinic uses the process of vitrification – rapid freezing at the temperature of -196 ˚C. Frozen embryos are stored in specialized liquid nitrogen capsules. Embryos are stored until the patient requires the use , for the maximum period of 5 years.
Sperm and testicular tissue can also be stored and kept for the future use in insemination and IVF program.
PATIENT INFORMATION
For all your doubts.
We strongly recommend reading it and noting any possible questions. This should help with processing high information load.
It is important to remember that every patient has different reaction to the therapy and treatment, and that every cycle is special in its own way.
This means that every patient will respond differently to the therapy when compared to others. Moreover, every individual patient may have different response in different treatment cycles. For this reason, patient may discover the difference between ones own treatment and treatments of others.
Please do not attempt to compare your treatment with other patients. Even though patients feel they can relate to one another, it is important to remember that IVF fertilization is very private issue.
Infertility is not rare. Estimates show that 10% of couples experience low to high difficulty in creation of offspring.
In-Vitro fertilization is preformed only when no other simpler method of sterility treatment is applicable, ant it is preformed in laboratory.
Pregnancies achieved through IVF are completely same as natural pregnancies, and therefore complications may arise regardless of the procedure.
The process does not guarantee pregnancy. It is sometimes necessary to go through the process of IVF fertilization several times before success.
The success rate of this method is dependant on many factors and couple related specificities, and its estimated at between 25% and 40%.
THERE ARE TWO PRINCIPAL KINDS OF INVITRO FERTILIZATION:
Classic In Vitro fertilization method (IVF) consists of adequate preparation, follicular stimulation, puncture, cellular aspiration and subsequent insemination.
This process should (but it doesn’t always) result in fertilization and creation of one or more fertilized cells.
The rest of the process consists of monitoring embryo growth and development , its subsequent intra uterine placement, as well as the embryo acceptance and further growth.
Microfertilization (ICSI) is technologically significantly more complicate. The method of merging egg cells and spermatozoid is done through micromanipulation – sperm cell is introduced directly into the egg cell using specialized equipment.
This procedure is indicated for the patients of older age with low number of egg cells, and in cases of low sperm count and/or mobility .
Finally, the procedure is used in cases of repulsion between the sex cells, exemplified by spermatozoid inability to find a way to the egg cell under the classical IVF conditions.
Microfertilization is sometimes complemented with testicular aspiration biopsy (TESA) or surgical biopsy. This is preformed with cases with insufficient sperm cells in ejaculate.
Decision about the method selection depends on number of factors, the most important ones being:
- Age of female patient and length of infertile period
- Number and quality of egg cells.
- Number and quality of spermatozoids.
- History of unsuccessful attempts
Definitive decision is made through patient-doctor consultation, and with patients informed approval. It is therefore crucial that the patient is properly informed about all the relevant elements of the procedure.
Nakon specijalističkog pregleda se pristupa neophodnim pretragama i analizama, koje pacijenti mogu obaviti u okviru naše bolnice.
Pošaljite zahtjev
prof dr Aleksandar Ljubić

Aleksandar Ljubić rođen je 1958. godiine u Beogradu, gdje je završio školovanje, postdiplomske, magistarske i doktorske studije. Svoje profesionalno usavršavanje nastavio je u SAD-u, Japanu, Velikoj Britaniji i Italiji.
Radno iskustvo:
2015 – Zamjenik Generalnog sekretara Svjetske asocijacije za perinatalnu medicinu;
2013 – 2014 Medicinski direktor Medigroup-e;
2009 – Predsjednik Upravnog odbora Klinike za dječiju neurologiju;
1995 – 2013 Medicinski fakultet u Beogradu, kao asistent, docent, potom i vanredni profesor ginekologije i akušerstva;
Profesor je i na DIU (Dubrovnik International University);
2004 – 2013 Klinički Centar Srbije, prvo kao pomoćnik direktora, potom i kao direktor Klinike za Ginekologiju i akušerstvo;
1986 – 2013 Klinika za ginekologiju i akušerstvo, Klinički centar Srbije; 13 godina načelnik odeljenja carskih rezova i visokorizičnih trudnoća.
Reference / stručnu radovi / članstva:
Rukovodilac 10 međunarodnih i nacionalnih naučnih projekata i autor preko 450 članaka i 25 knjiga;
Član uredništva u 6 stručnih časopisa;
Potpredsjednik stručnog savjeta Kliničkog Centra i koordinator izgradnje nacionalnog biotehnološkog centra;
Predsjednik Udruženja za ultrazvuk Srbije, osnivač i prvi direktor srpske grane internacionalne škole za ultrazvuk “Ian Donald”;
Dugogodišnji predsjednik Republičke komisije za vantelesno oplođenje i potpredsjednik Republičke komisije za perinatalnu medicinu;
Član međuodeljenskog odbora SANU za humanu reprodukciju.


